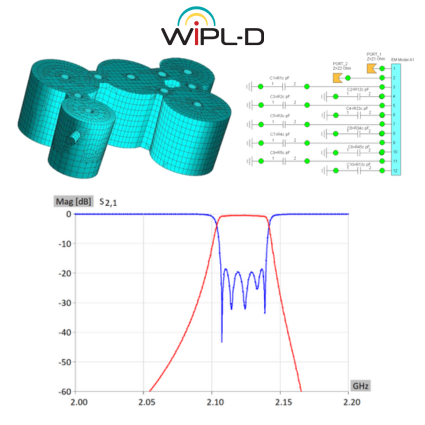
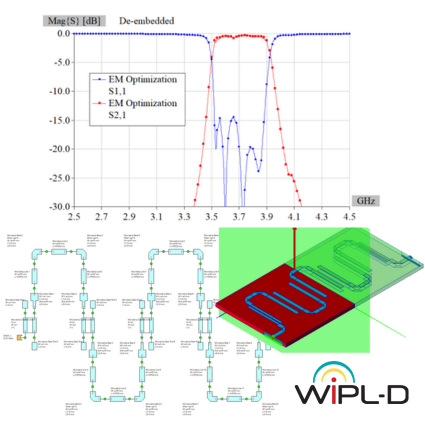
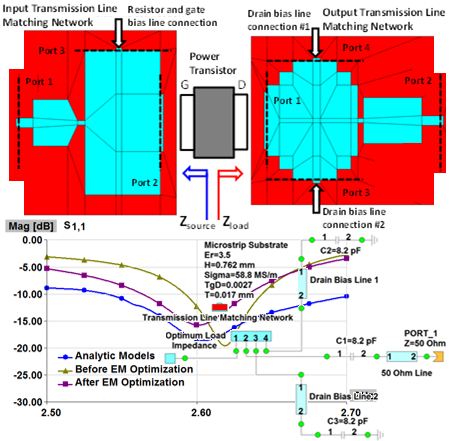
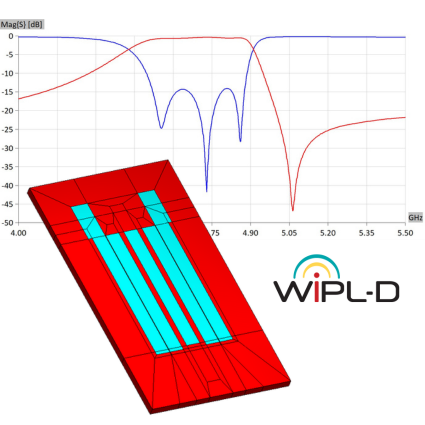
Cavity Filter Design and Optimization
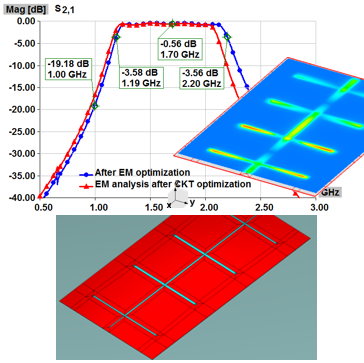
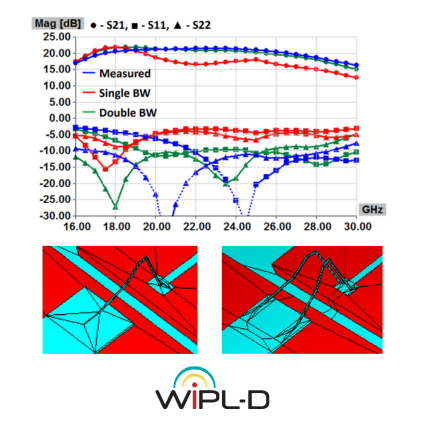
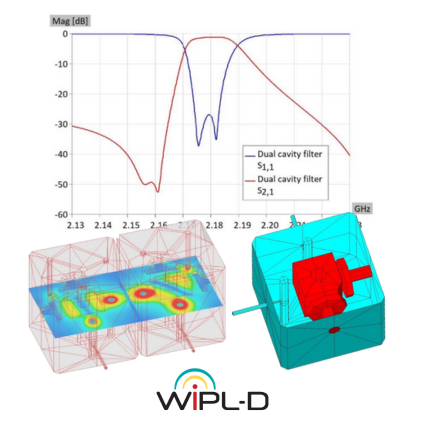
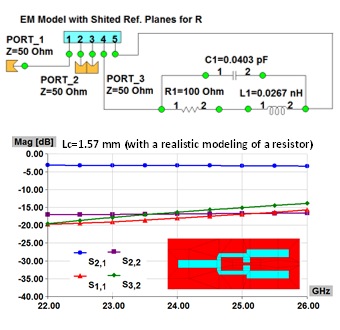
This application note demonstrates extremely efficient interoperability of WIPL-D software: WIPL-D Pro CAD, WIPL-D Microwave Pro, WIPL-D Pro, and WIPL-D Optimizer—for design, modeling, simulation, and optimization of cavity filters. A complex 2.1 GHz five-cavity pass-band filter is imported, meshed, and simulated in WIPL-D Pro CAD and WIPL-D Pro, then optimized in WIPL-D Microwave Pro with WIPL-D Optimizer. EM simulation is done once, while optimization uses a combined 3D/circuit model, where tuning capacitors emulate screw adjustments, enabling fast, precise tuning. WIPL-D supports simplified geometries in WIPL-D Pro or detailed CAD-imported models in WIPL-D Pro CAD, offering flexibility, accuracy, and speed for advanced filter design.