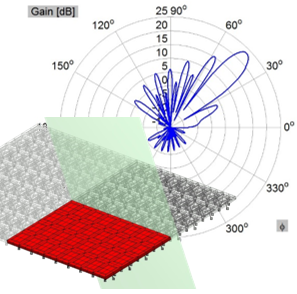
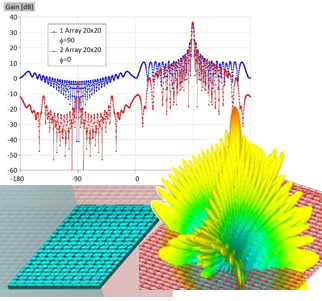
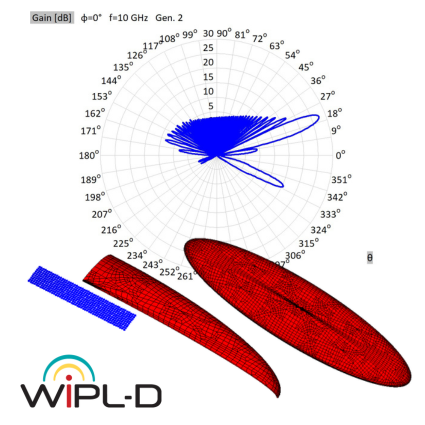
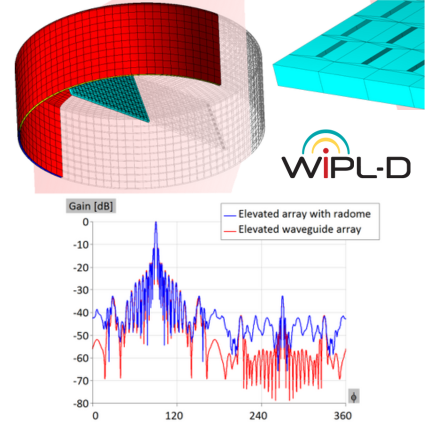
Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA)
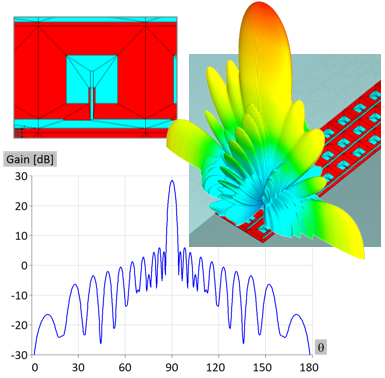
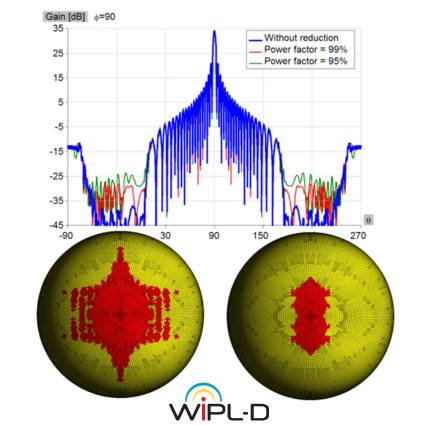
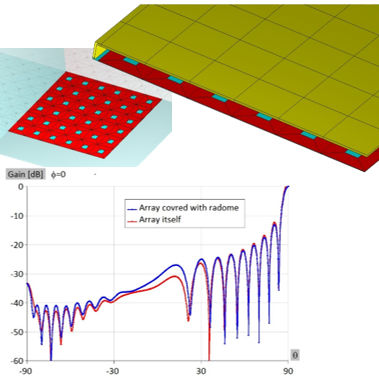
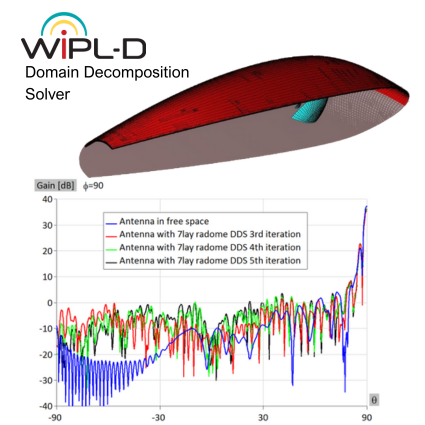
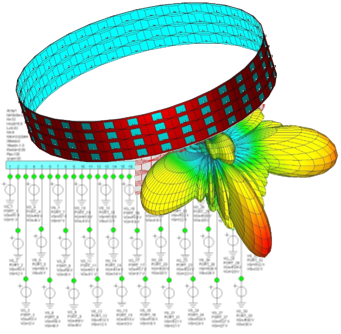
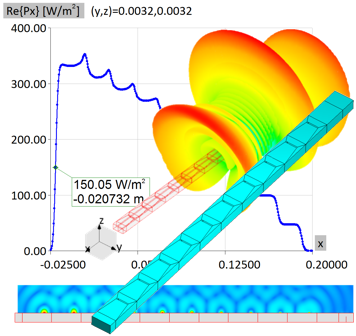
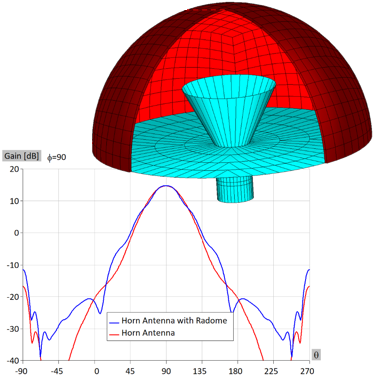
Microwave engineering often focuses on designing antenna arrays for satellite and mobile systems, where AESA architecture enables rapid electronic beam steering without mechanical movement. WIPL-D Pro, as a full-wave MoM solver, employs higher-order basis functions, quadrilateral meshing, efficient CPU/GPU acceleration, and smart symmetry handling to analyze large arrays. With asymmetric excitations, users can assign different voltages to elements for multiple steering angles without re-running the EM simulation. A typical example is a 128-element stacked patch array with three dielectrics and four coaxial probes per element, which runs in just a few minutes on a standard desktop PC while delivering stable, consistently accurate results.