Ultra-Wide Band Elliptical Antenna
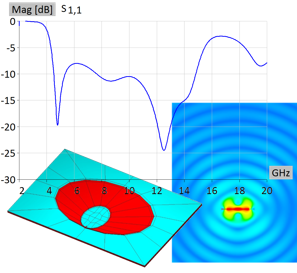
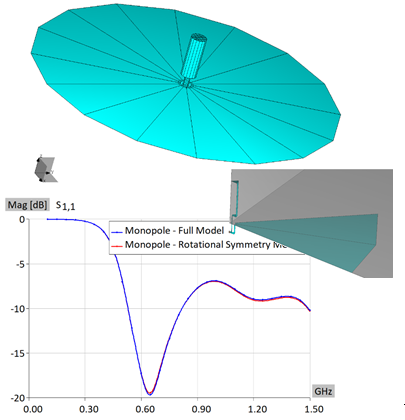
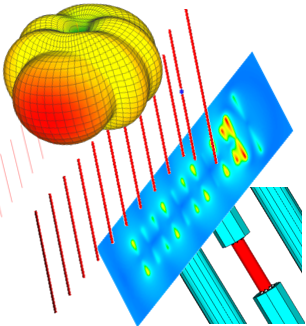
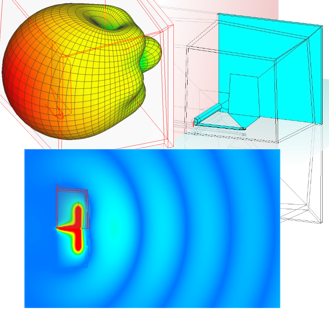
The application note presents the simulation of a UWB elliptical antenna, covering 5–14 GHz. The antenna is electrically small and requires few unknowns. Simulation results demonstrate accurate performance across the frequency band, with VSWR, radiation patterns, and key parameters. Several features improve simulation time: usage Method of Moments with higher order basis functions, symmetry halving unknowns, and reduced frequency points via built-in interpolation, ensuring fast, accurate results for complex designs. Although WIPL-D is a frequency-domain solver, it handles UWB antennas efficiently. With execution on multicore CPUs, simulations run on an inexpensive desktop quad-core PC and last only a couple of seconds per frequency point.