Cross Spiral Antenna (CSA)
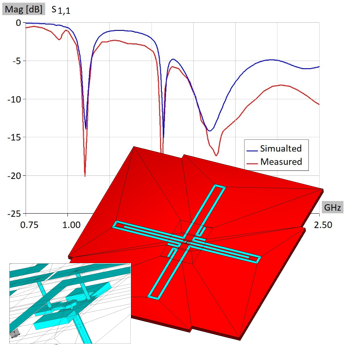
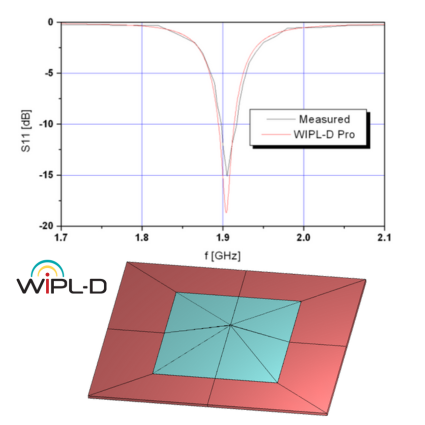
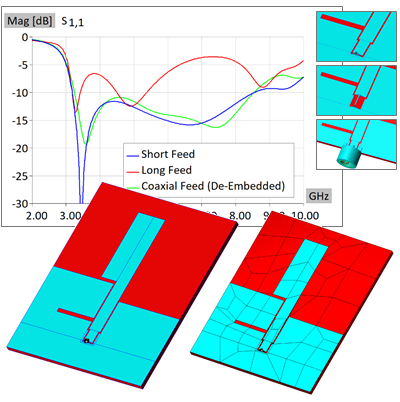
This note presents the design and simulation of a Cross Spiral Antenna (CSA), a planar antenna, based on the paper “A multi-polarization multi-band cross spiral antenna for mobile communication devices”, ISAP 2012. The CSA exhibits good performance at three frequency bands, intended for combined RFID, mobile-phone (UMTS), and GPS applications at 1.0 GHz, 1.8 GHz, and 1.67 GHz, respectively. The printed device is fabricated on low-cost FR4 substrate (Er = 4.4, Hsub = 1.6 mm). The feeding area was realized in two ways: a simple wire bridge and a coaxial feed with connector. Both approaches yielded stable, similar results. Simulations were performed on a standard desktop PC, with times measured in seconds, showing agreement with measured data.