Substrate Integrated Waveguide Cavity-Backed Slot Antenna
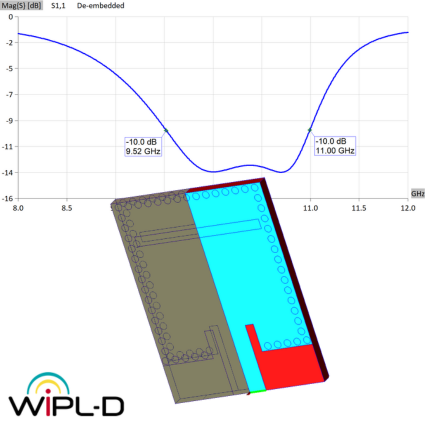
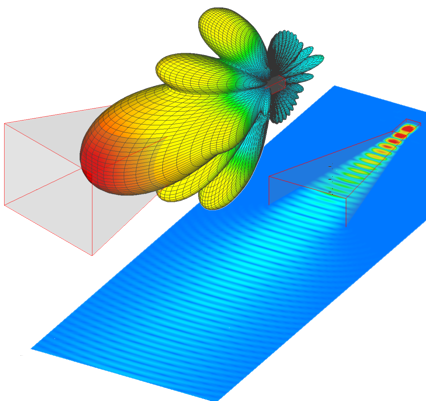
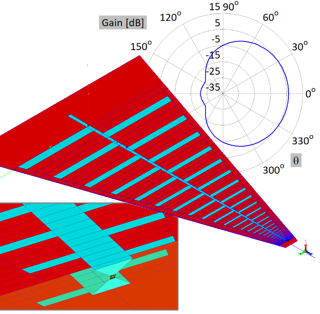
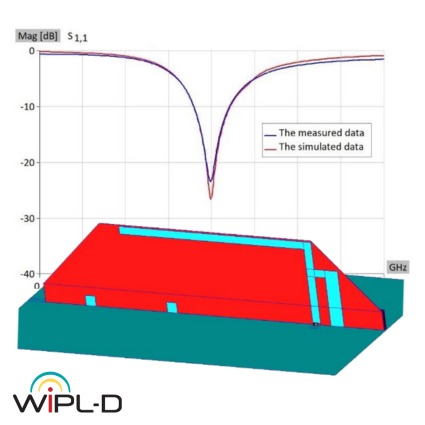
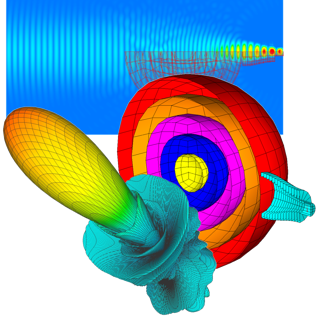
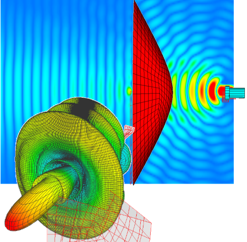
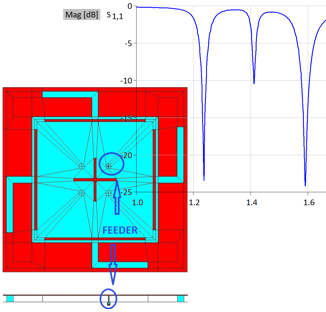
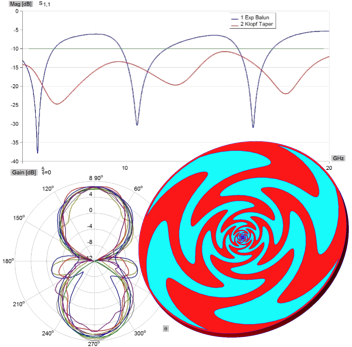
This application note describes the design and full-wave simulation of a Substrate Integrated Waveguide (SIW) Cavity-Backed Slot Antenna using WIPL-D Pro CAD. The antenna operates in the 8-12 GHz (X-band), with return loss, radiation pattern, gain, and near-field distribution as key results. The model is implemented on a Rogers RT/duroid 5880 substrate, with the SIW structure realized by metallic vias designed to suppress leakage. WIPL-D’s Method-of-Moments solver, combined with quadrilateral meshing and higher-order basis functions, enables accurate analysis with a low number of unknowns. Symmetry, optimized geometry definition, and built-in CPU/GPU acceleration provide fast and reliable antenna simulations on a standard desktop PC.