Synthetic Aperture Radar Systems
04-Dec-2017

04-Dec-2017
 Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is a technique which uses signal processing to improve the resolution beyond the limitation of physical antenna aperture. In SAR, physical movement of the actual antenna is used to synthesize electrically large antenna aperture.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is a technique which uses signal processing to improve the resolution beyond the limitation of physical antenna aperture. In SAR, physical movement of the actual antenna is used to synthesize electrically large antenna aperture.
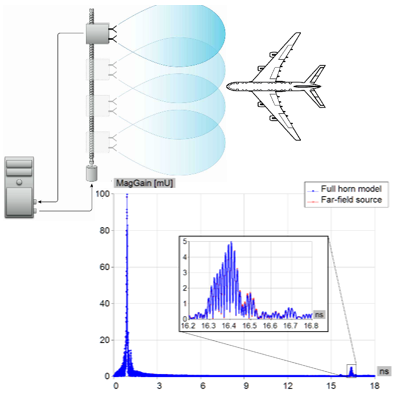
Application note describes efficient numerical analysis of rail SAR system. The approach is based on MoM-SIE using higher order basis functions, reductions of unknown coefficients needed for the analysis, and the far-field equivalent sources.
The simulation was additionally speed up by using multi GPU platform, where each frequency point is simulated at single inexpensive GPU card. For the GPU expander with 8 identical GPU cards, the simulation time has been increased roughly 8 times.
By replacing real radar antenna by an equivalent far-field source, the problem with different transceiver positions is reduced to multi‑excitation problem. Instead to increase simulation time 101 times for 101 position, the simulation time was only increased two times. As an example, 40 wavelengths long airplane was illuminated from 101 SAR antenna positions in around 9 hrs.
Section: Radar Cross Section / Scattering
For full version of the document, please check the following pdf.