Microwave Imaging Systems for Medical Applications
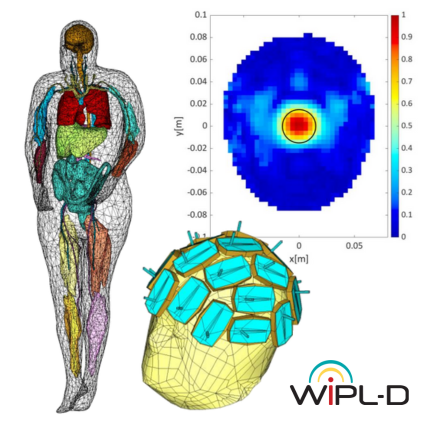
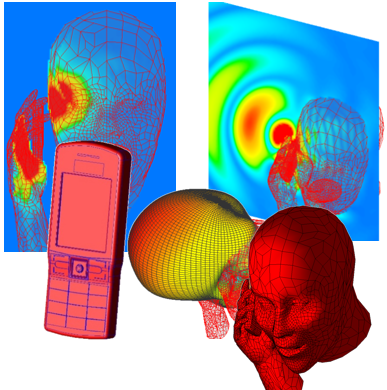
A fully functional module for microwave imaging is implemented in WIPL-D Pro 3D EM simulation environment. Software enables creation of anthropomorphic phantoms from STL files, converting triangular meshes to quadrilateral meshes to improve accuracy and reduce computational load. A semi-automatic antenna placement positions antennas optimally around the head while avoiding intersections. The imaging scenario is simulated at 1 GHz, and differential S-parameters are analyzed directly and via the TSVD algorithm. Simulations with and without stroke allow detection, localization, and size estimation, showing that WIPL-D provides an efficient and accurate solution for EM-based microwave brain imaging research and medical diagnostics.